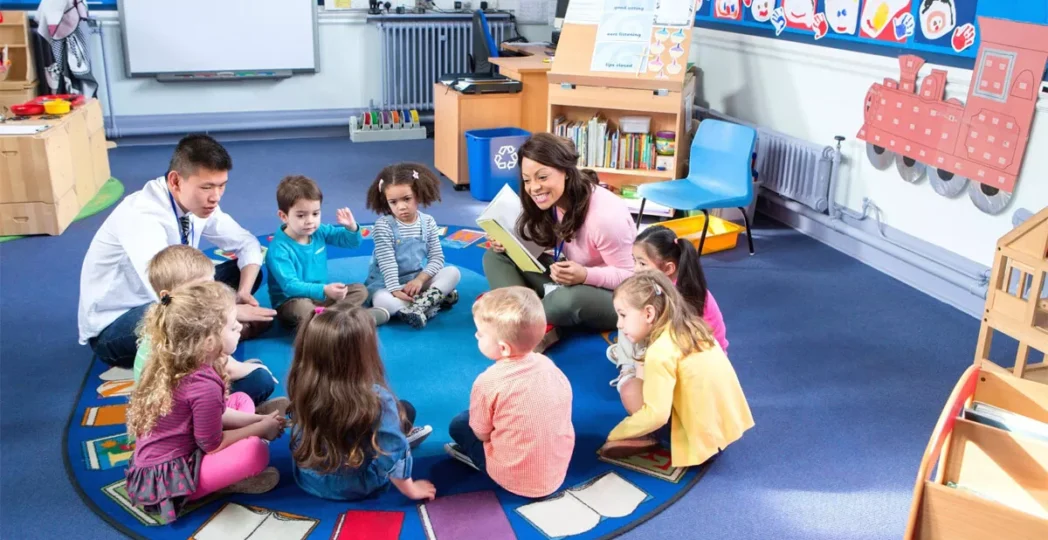
Introduction
In this article, we will explore what an early years practitioner does, how to become one, and what you can expect in terms of career prospects, including job security and salary expectations. Whether you are considering a direct entry into childcare, contemplating an apprenticeship, or aiming to gain a formal qualification like a Level 2 or Level 3 diploma in childcare, this guide will provide you with all the necessary information to make an informed decision about this vibrant and fulfilling career path.
What Does an Early Years Practitioner Do?
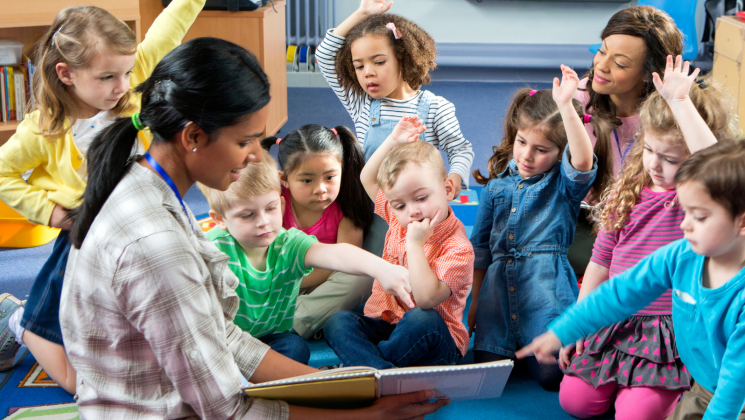

- Educational Activities: They plan and conduct educational activities that promote the cognitive and social development of children. This could include anything from reading stories and teaching basic numbers and letters to organizing arts and crafts sessions.
- Physical Development: Practitioners often facilitate physical activities that help develop motor skills. Examples include supervised play on playgrounds or leading exercises that are age-appropriate and fun.
- Emotional Support: They provide emotional support and guidance to children, helping them develop confidence and social skills. This is done through consistent positive reinforcement, encouragement, and patient interaction.
Examples from the Field:
- Sarah, an early years practitioner in a busy city nursery, sets up a ‘mini-world’ play area every week, where children engage in role-playing that stimulates their imagination and communication skills. This activity not only keeps the children engaged but also aids in developing their language and social interaction skills.
- Tom, working in a rural preschool, incorporates outdoor learning activities that involve nature walks and exploration. His approach uses the local environment, teaching children about wildlife, plants, and the seasons, enhancing their observational and reasoning abilities.
- Jenna, a special needs early years educator, uses tailored educational tools to support children with additional needs. She employs sensory play materials to help children with autism spectrum disorders enhance their sensory integration skills.
These examples show how varied the role of an early years practitioner can be, tailored to meet the needs of different settings and individual children. The adaptability and creativity required in this profession make it both challenging and rewarding.
Types of Settings for Early Years Practitioners:
- Nurseries and Daycare Centers: These are common workplaces for early years practitioners, where they work with groups of children in structured settings.
- Pre-schools: Similar to nurseries but often with a stronger educational focus, preparing children for the transition to primary school.
- Private Households: Some practitioners work in private homes, providing personalized childcare and learning activities for children in a home environment.
By understanding the scope of their responsibilities and the settings in which they can work, those interested in this field can better envision their day-to-day roles and the impact they can have on young learners. Whether through structured educational programs or more informal play-based learning, early years practitioners are essential to fostering young children’s development during these formative years.
Salary Expectations for Early Years Practitioners
One of the most common inquiries about pursuing a career in early years education concerns the financial aspect—specifically, what one can expect to earn in this vital role. Salary for early years practitioners in the UK varies based on several factors including experience, location, and the specific workplace setting. Here’s a closer look at the typical salary ranges:
Table of Salary Expectations
| Role | Experienced Salary (£) |
|---|---|
| Early Years Practitioner | 18,000 to 23,000 |
| Nursery Assistant | 17,000 to 22,000 |
| Early Years Teacher | 30,000 to 47,000 |
| Childcare Worker | 18,500 to 23,000 |
For more details, check the UK government website for early years teachers.
Influencing Factors:
- Experience: Salaries typically start on the lower end but can increase significantly with experience and additional qualifications.
- Location: Urban areas, especially cities like London, often offer higher salaries due to the higher cost of living and greater demand for childcare services.
- Qualifications: Higher qualifications can lead to better-paying positions and opportunities for advancement.
UK Government Support
The UK government recognizes the importance of early years education and supports the sector through funding and regulatory frameworks. This backing helps maintain high standards of care and education while also ensuring that jobs in this sector are well-structured and supported. Furthermore, initiatives like funded apprenticeships and training programs are available, which help individuals gain the necessary qualifications while working, thus enhancing their career prospects and potential earnings.
Job Security and Career Advancement
Job Security: The demand for early years practitioners remains consistently high in the UK, providing substantial job security for those in the profession. This stability is largely due to the essential nature of childcare and early education services, which are critical for working parents and guardians. Furthermore, government regulations require a specific ratio of qualified caregivers to children, ensuring ongoing demand for these roles.
Career Advancement: For those looking to advance in their early years career, there are numerous paths to explore:
- Specializations: Gain expertise in areas like special education needs (SEN), outdoor learning, or Montessori methods.
- Leadership Roles: Progress to positions such as nursery manager, early years teacher, or even open your own childcare business.
- Higher Education: Pursue further studies, such as early years degrees, to open doors to higher-level educational roles or policy-making positions.
Pathways to Becoming an Early Years Practitioner
On-the-Job Training: Starting as an apprentice or an assistant in a nursery or preschool can be a great way to enter the field without prior qualifications. Many facilities offer the opportunity to earn qualifications on the job, such as NVQs or SVQs in Childcare.
Apprenticeships: Apprenticeships are a fantastic way to combine learning and earning. These programs typically involve working under the supervision of experienced staff while studying towards a formal qualification, such as:
- Level 3 Early Years Educator (equivalent to A Levels)
Educational Programs: For those preferring a more traditional educational route, numerous colleges and universities offer relevant courses. Potential qualification include:
- Level 3 Diplomas in Childcare
Fast-Track Your Career in Childcare with a Level 3 Qualification
Special Offer: Enroll in our course at the Centre of Excellence across the UK and benefit from our JOB GUARANTEE or money-back offer.
Conclusion
Choosing a career as an early years practitioner is not only fulfilling but also a wise professional move, given the robust job security and myriad opportunities for advancement. The role allows you to make a significant impact during the crucial developmental stages of a child’s life while offering a stable and progressive career path.
For those inspired to take the first steps towards this rewarding career, it’s advisable to explore the various training and qualification options available. Whether through on-the-job training, apprenticeships, or formal education, the early years sector is accessible and ripe with potential for dedicated individuals.
FAQs on Becoming an Early Years Practitioner
- What is an early years practitioner? An early years practitioner is a trained professional who works with children from birth to five years old, providing educational activities and care that support their development and learning during these crucial early years.
- How can I become an early years practitioner in the UK? To become an early years practitioner in the UK, you typically need to gain a relevant qualification, such as a Level 2 or Level 3 Diploma in Childcare, which can be pursued through various educational pathways including colleges, apprenticeships, and online courses.
- What qualifications are needed to become an early years practitioner? The essential qualifications for becoming an early years practitioner usually include a Level 3 Diploma in Childcare. This qualification prepares you to work independently in a range of childcare settings.
- How to become an early years teacher in the UK? To become an early years teacher in the UK, you need to complete an Early Years Initial Teacher Training (EYITT) programme, which is specifically designed for those who wish to specialize in early childhood education.
- What are the responsibilities of an early years practitioner? Early years practitioners are responsible for planning and delivering educational activities, supporting children’s development (social, cognitive, and physical), and ensuring a safe and nurturing environment.
- Is there a demand for early years practitioners in the UK? Yes, there is a consistent demand for early years practitioners in the UK due to ongoing governmental support for early childhood education and the need for qualified professionals in nurseries and preschools.
- What career opportunities are available after becoming an early years practitioner? After becoming an early years practitioner, career opportunities include roles such as nursery manager, pre-school leader, or special educational needs coordinator. With further qualifications, moving into early years teaching or even opening your own childcare service are viable paths.


